Chainlink Keepers Architecture
Overview
Chainlink Keepers allow smart contracts to outsource regular maintenance tasks in a trust minimized and decentralized manner. The network aims to provide a protocol for incentivization of execution and governance of execution within the Keeper ecosystem.
There are three main actors in the ecosystem:
- Upkeeps: These are the maintenance tasks that smart contracts need external entities to service for them. These tasks are just functions on a smart contract and these contracts should be Keepers-compatible.
- Keepers registry: The contract through which anyone can register, and manage, their Upkeeps.
- Keepers: Nodes in the Keepers Network that service registered and funded Upkeeps in the Keepers registry.
The diagram below describes the architecture of the Keeper network. It is responsible for governing the actors on the network and compensating Keepers for performing successful Upkeeps. Clients can register for Upkeep and node operators can register as Keepers.
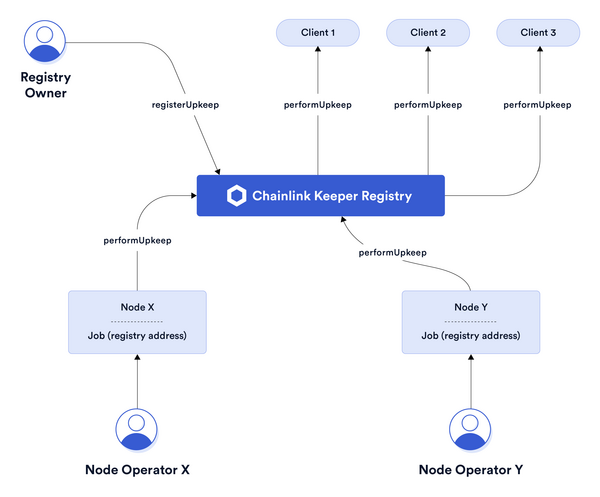
Keeper Contracts
There are several contracts to be aware of. You can find them in the Chainlink repository. For details on how to use them see the Keepers-compatible Contracts page.
KeeperCompatible.sol(link): Imports the following contracts:KeeperBase.sol(link): Enables the use of thecannotExecutemodifier. Import this contract if you need for this modifier. See thecheckUpkeepfunction for details.KeeperCompatibleInterface.sol(link): The interface to be implemented in order to make your contract Keepers-compatible. Import this contract for type safety.
KeeperRegistry.sol(link): The registry contract that tracks all registered Upkeeps and the Keepers that can perform them.UpkeepRegistrationRequests.sol(link): The registration contract that allows users to register and configure their Upkeep with the associatedKeeperRegistrycontract.
How it works
Keepers take responsibility for Upkeeps in turns. Each turn is counted in blocks. See the configuration section to find the current block count per turn for your network. The registered Upkeeps are broken into buckets based on the number of Keepers on the network. At the end of each turn, the buckets rotate from one Keeper to the next. Even if a Keeper goes down, we have built-in redundancy and your Upkeep will be performed by the next Keeper in line.
During every block the Keeper will check if the Upkeep is eligible using off-chain compute (a simulation), and then broadcast them on-chain when eligible.
Once a Keeper has performed an Upkeep, it cannot do so again until another Keeper on the network has subsequently performed the same Upkeep. This protects against a faulty or malicious Keeper from taking repeated action on a given Upkeep.
Supported Networks and Cost
For a list of blockchains that is supported by Chainlink Keepers, please review the supported networks page. To learn more about the cost of using Chainlink Keepers, please review the Keepers economics page.